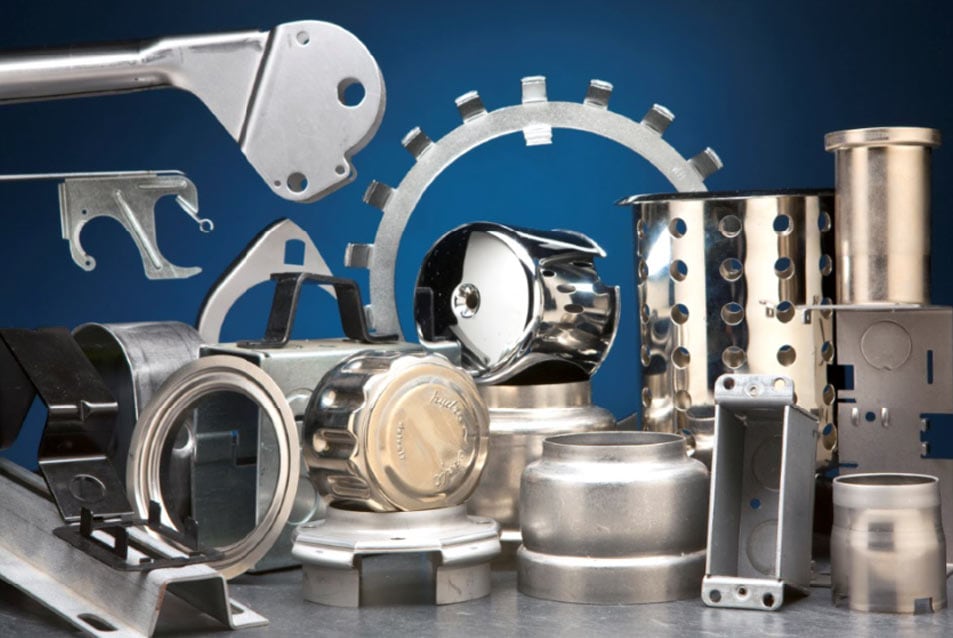
Stamping dies are essential tools in the manufacturing industry, used to shape, cut, and form sheet metal into precise components. Depending on the complexity and requirements of a project, manufacturers typically choose between three main types of stamping dies: progressive, compound, and transfer dies. Each type has unique capabilities, costs, and maintenance needs. In this blog, we will explore these differences and highlight how Larson Tool takes a distinct approach to stamping, setting us apart from other industry players.
1. Progressive Dies
Progressive dies are designed for high-volume production of complex parts. This type of die operates through a series of sequential stations, each performing a specific operation on the workpiece as it moves through the press.
How It Works:
- A strip of metal feeds into the die and moves through various stations.
- At each station, a different operation is performed, such as cutting, bending, or punching.
- By the end of the process, a completed part is separated from the strip.
Cost of Design and Production
Progressive dies are known for their higher upfront design and tooling costs. The complex nature of the die requires meticulous planning and precision engineering. However, the cost per part decreases significantly with large production runs, making this option highly cost-effective for long-term projects.
Maintenance
Progressive dies demand regular maintenance due to their intricate structure and the multiple operations involved. Preventative maintenance is critical to avoid costly downtime and ensure consistent quality.
Advantages of Progressive Dies:
- High production speed and efficiency.
- Minimal material waste.
- Ideal for producing complex parts in large volumes.
Drawbacks Of Progressive Dies:
- High initial investment.
- Limited flexibility for design changes.
2. Compound Dies
Compound dies perform multiple operations, such as cutting and punching, in a single stroke of the press. This type of die is commonly used for simple, flat parts.
How It Works:
- The entire operation is completed in one press stroke.
- Typically, compound dies are used for operations requiring high precision in a single plane.
Cost of Design and Production:
Compound dies are generally less expensive to design and produce compared to progressive dies. The simplicity of the die reduces upfront costs, but the process is less suitable for complex or high-volume projects.
Maintenance:
Due to their simpler structure, compound dies require less maintenance than progressive dies. Regular inspection of cutting and punching components ensures continued accuracy and longevity.
Advantages of Compound Dies:
- Lower initial tooling cost.
- High precision for single-plane operations.
- Efficient for small to medium production runs.
Drawbacks of Compound Dies:
- Limited to simpler part designs.
- Not cost-effective for high-volume production.
3. Transfer Dies
Transfer dies are used for large or intricate parts that require multiple operations. Unlike progressive dies, transfer dies move the workpiece independently between stations using mechanical transfer systems.
How It Works:
- A blank is cut and then transferred through various stations for forming, bending, or other operations.
- Each station is independent, allowing for complex shapes and larger parts.
Cost of Design and Production:
Transfer dies involve higher tooling and setup costs due to their complex transfer mechanisms. They are best suited for medium to high production runs, where the versatility and capability to handle complex parts justify the investment.
Maintenance:
The sophisticated nature of transfer dies requires regular maintenance of both the die and transfer mechanisms. This ensures smooth operation and prevents misalignment or part defects.
Advantages of Transfer Dies:
- Capable of producing large or complex parts.
- Greater flexibility compared to progressive and compound dies.
- Ideal for projects requiring multiple forming operations.
- Less material is used in a Transfer die due to the lack of a connection web used to carry the part through the process. Transfer grippers take the place of the carrying web saving material on each part. This reduced amount of material used saves costs on the overall piece price.
Drawbacks of Transfer Dies:
- High initial cost.
- Longer setup times.
Comparing Costs: Design, Run, and Maintenance
| Die Type | Design & Tooling Cost | Production Cost Per Part | Maintenance Needs |
| Progressive | High | Low (for large volumes) | Regular and intensive |
| Compound | Medium | Medium | Low to moderate |
| Transfer | High | Medium | High |
How Larson Tool Stands Out
At Larson Tool, we pride ourselves on offering innovative and customer-centric solutions that differentiate us from other stamping companies. Here’s how our approach stands out:
1. Collaborative Design Process:
We work closely with our clients from the initial concept to final production. By understanding your unique needs, we can recommend the most suitable die type and optimize the design for cost, quality, and efficiency.
2. Advanced Technology:
Larson Tool leverages state-of-the-art technology and precision engineering to deliver superior stamping solutions. Our facilities are equipped with advanced machinery that ensures high accuracy and consistent results across all types of dies.
3. Commitment to Quality:
Quality is at the core of everything we do. Our rigorous inspection processes and adherence to industry standards guarantee that every part meets or exceeds expectations.
4. Cost-Effective Solutions:
We understand that managing costs is critical for our clients. By optimizing material usage, minimizing waste, and offering competitive pricing, Larson Tool ensures you get the best value for your investment.
5. Exceptional Maintenance Programs:
Our preventative maintenance programs are designed to maximize the lifespan of your tooling and minimize downtime. Regular maintenance checks and prompt repairs keep your operations running smoothly.
6. Customization and Flexibility:
Unlike many stampers that follow a one-size-fits-all approach, Larson Tool tailors our services to your specific requirements. Whether you need a progressive, compound, or transfer die, we deliver customized solutions that align with your goals.
7. Experienced Team:
Our team of skilled engineers and technicians brings decades of experience to every project. Their expertise ensures precision and efficiency at every stage of production.
Conclusion
Choosing the right type of stamping die is critical to the success of your manufacturing project. While progressive dies offer speed and efficiency for high-volume runs, compound dies provide precision for simpler parts, and transfer dies excel in producing large or complex components. Each type has distinct costs and maintenance requirements, making it essential to evaluate your needs carefully.
At Larson Tool, we go beyond standard stamping services to deliver tailored solutions that prioritize quality, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. With our collaborative approach, cutting-edge technology, and commitment to excellence, we help our clients achieve outstanding results in every project. Contact us today to learn more about our stamping capabilities and how we can meet your manufacturing needs.
About Larson Tool & Stamping Company
Since its inception in 1920 in Attleboro, MA, Larson Tool & Stamping Company has been making a difference as a valued supplier of precision metal stampings and assemblies to hundreds of companies in the United States. Larson provides high-quality, cost-effective solutions with our wide range of capabilities that include forming, stamping, deep drawing, machining, assembly, brazing, coining, and water-jetting. Through significant investment in leading-edge manufacturing equipment and the loyal support from customers and co-workers, Larson perpetuates the commitment made by our founders to do whatever is necessary to meet and exceed customer expectations.
Find out first-hand and contact us now to see for yourself.